873. Palindromes
Non-empty string containing
a certain word is called palindrome if it reads the same from left to right and
from right to left.
Let we are given a word s, consisting of n uppercase letters of Latin alphabet. Deleting from the word
a certain set of characters, you can get the palindrome string. Find the number
of ways to delete from the word some (possibly empty) set of symbols so that
the resulting string is a palindrome. Ways in different order of deleting
characters are considered equal.
Input. One string s of length n (1
≤ n ≤ 60).
Output. Print the number of ways to
get a palindrome.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
BAOBAB |
22 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let dp[i][j] stores
the number of palindromes that can be obtained from the substring si
sj by deleting letters. Then dp[i][i] = 1, since a word of one character is
a palindrome.
Let si = sj = X, substring si
sj has the form XPX. Here
P denotes
the substring si+1
sj-1. Split the palindromes of the
string
XPX into non-overlapping groups:
·
include the left X and do not include the right X. The
number of palindromes equals to the number of palindromes in string XP
minus the number of palindromes in P, that equals to dp[i][j 1] dp[i + 1][j 1];

·
include the right X
and do not include the left X. The number of palindromes
equals to the number of
palindromes in string PX minus the number of palindromes in P, that equals
to dp[i
+ 1][j] dp[i + 1][j 1];
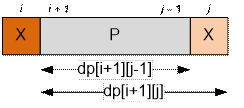
·
the palindromes of the string P. Their
number equals to
dp[i + 1][j 1]. However,
with each palindrome Q of string P, we can construct the XQX palindrome. The number of palindromes of the form XQX will also be dp[i + 1][j 1].

·
palindrome XX (one palindrome).
![]()
The total number of palindromes for the case si = sj is
(dp[i][j 1] dp[i + 1][j 1]) +
(dp[i
+ 1][j] dp[i + 1][j 1]) +
2 * dp[i
+ 1][j 1] +
1
= dp[i][j 1] + dp[i + 1][j] + 1.
Let si ≠ sj, substring si
sj has the form XPY (si = X, sj = Y). Split
the palindromes of the string XPY into non-overlapping groups:
·
include the symbol X and do not include the symbol Y. The number of palindromes
equals to the number of
palindromes in string XP minus the number of palindromes in P, that equals
to dp[i][j 1] dp[i + 1][j 1];

·
include the symbol
Y and do not include symbol
X. The
number of palindromes equals to the number of palindromes in string PY minus the
number of palindromes in P, that equals to dp[i + 1][j] dp[i + 1][j 1];
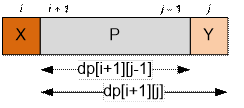
·
palindromes of the string P. Their
number is dp[i
+ 1][j 1].

The total number of palindromes for the case si ≠ sj is
(dp[i][j 1] dp[i + 1][j 1]) +
(dp[i
+ 1][j] dp[i + 1][j 1]) +
dp[i
+ 1][j 1]
= dp[i][j
1] + dp[i + 1][j] dp[i + 1][j 1].
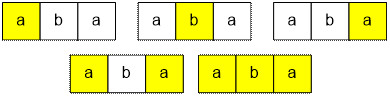
Example
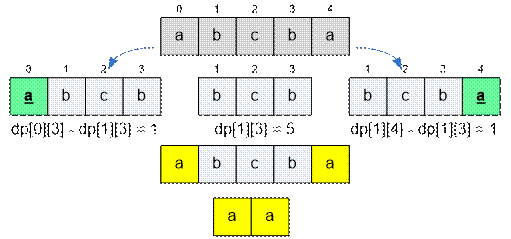
By deleting the letters from the string aba, you can get 5 palindromes.
Consider the string abab = s0s1s2s3. Since s0
≠ s3, the substring s0
s3 has the form XPY. Hence dp[0][3] =
(dp[0][2] dp[1][2]) +
(dp[1][3]
dp[1][2]) +
dp[1][2] =
= dp[0][2] + dp[1][3] dp[1][2] = 5 + 5 2 = 8.
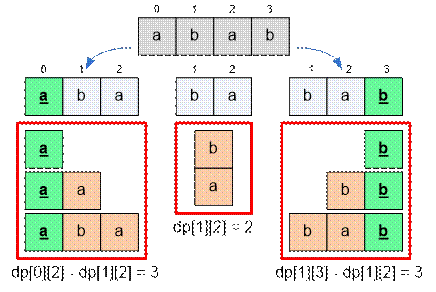
Consider the string abcba = s0s1s2s3s4. Since s0 = s4, the
substring s0
s4 has
the form
XPX. Hence dp[0][4]
=
(dp[0][3] dp[1][3]) +
(dp[1][4]
dp[1][3]) +
2 * dp[1][3] +
1 =
= dp[0][3] + dp[1][4] + 1 = 6 + 6 + 1 = 13.
Algorithm realization
Store the input
string in the array s. Declare an array
dp.
#define MAX 65
char
s[MAX];
long long dp[MAX][MAX];
Read
the input string s. Fill dp[i][i]
= 1.
gets(s);
n = strlen(s);
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(i
= 0; i < n; i++) dp[i][i] = 1;
Iterate
over the lengths of the substrings len
and their starting positions
i.
for(len
= 1; len < n; len++)
for(i
= 0; i + len < n; i++)
{
j = i + len;
For each such substring si
sj compute the value dp[i][j], the number of
palindromes that can be obtained from it by removing characters. Since the
substrings si
sj are iterated in increasing order of their
lengths, the dp values for
all subsegments of shorter length have already been calculated.
if (s[i] == s[j])
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j] + dp[i][j-1] + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j] + dp[i][j-1] -
dp[i+1][j-1];
}
Print
the answer.
printf("%lld\n",dp[0][n-1]);
Algorithm realization recursion
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 61
Store the input
string in the array s. Declare an array
dp.
char s[MAX];
long long dp[MAX][MAX];
int i, j,
len, n;
long long f(int i, int j)
{
If i
> j, there is no palindromes.
if (i > j) return 0;
A word of one
character is a palindrome, set dp[i][i] = 1.
if (i == j) return dp[i][j] = 1;
If the value of dp[i][j]
is already computed, return it.
if (dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];
Compute the value of dp[i][j]
depending on whether the symbols si and sj are the same.
if (s[i] == s[j])
dp[i][j] = f(i + 1, j) + f(i, j - 1) + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = f(i + 1, j) + f(i, j - 1) - f(i + 1, j - 1);
return dp[i][j];
}
int main(void)
{
The
main part of the program. Read the input string s. Initialize
array dp.
gets(s); n =
strlen(s);
memset(dp, -1, sizeof(dp));
Print
the answer.
printf("%lld\n", f(0, n - 1));
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static String s;
static long dp[][];
static long f(int i, int j)
{
if (i > j) return 0;
if (i == j) return dp[i][j] = 1;
if (dp[i][j] != -1) return dp[i][j];
if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j))
dp[i][j] = f(i + 1,j) + f(i,j - 1) + 1;
else
dp[i][j] = f(i + 1,j) + f(i,j - 1) - f(i + 1,j - 1);
return dp[i][j];
}
public static void
main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
s = con.nextLine();
int n = s.length();
dp = new long[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++)
dp[i][j] = -1;
System.out.println(f(0,n-1));
con.close();
}
}